Sustainability
We care about the environment.
We work for a more livable future.
Sustainability
Critical raw material

There are many issues related to the extraction of the minerals from which metals are extracted, both environmental, ethical, and commercial.
In fact, on an environmental level, the greatest impacts are related to soil and water contamination, air pollution, and a decrease in biodiversity.
At the ethical level, there are problems related to the scarcity of raw materials and the lack of safety regulations and laws prohibiting child labor and guaranteeing adequate wages.
At a commercial level, problems are related to monopolies by specific countries on certain raw materials, price fluctuations related to the current geopolitical situation, and the vulnerability of the supply chain.
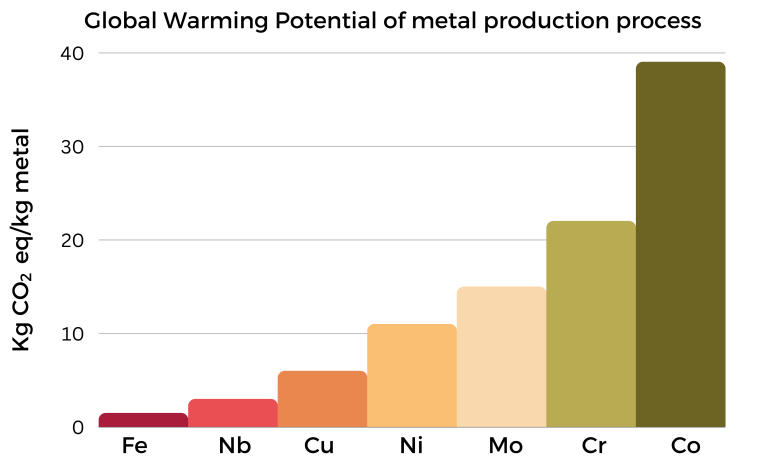
GLobal warming potential
The impacts relative to the CO2 and other GHG emissions, related to the mining operations and the refining of the ores until the production of the metals, are shown in the plot. They have been evaluated considering the data available in databases and using specific software created for LCA studies.
f3nice is able to reduce GHG emissions starting from metal scrap instead of virgin raw materials. The scrap comprises decommissioned industry components, obsolete parts from inventory, bulky scrap from the supply chain, and disqualified powder from 3D printing.

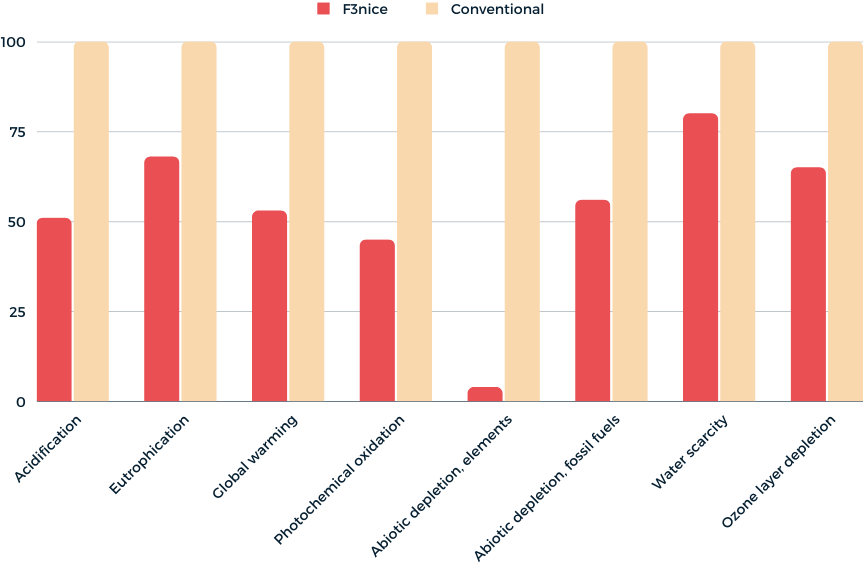
RESULT OF THE ANALYSIS PERFORMED WITH SIMAPRO

LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT ANALYSIS
A comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) analysis has been run between two production processes for the production of metal powder, used in the additive manufacturing industry.
The calculations have been performed with the help of LCA software and with adequate databases for the implementation of the models; the chosen method for the evaluation is EPD2018.
f3nice production process has lower impacts for all the impact categories: a significant reduction can be highlighted in the Global warming (GWP100a) category.
[kg SO2 eq]
Damages are caused by the formation and falling to the ground of acid rain due to the reaction of acid gases (NOx and SO2) with the water present in the atmosphere.
[kg PO43- eq]
Increase of chemical nutrients concentration in an ecosystem, which leads to abnormal productivity and excessive plant growth which causes severe reductions in water quality and animal populations.
[kg CO2 eq]
Change in global temperature is caused by the greenhouse effect that the release of greenhouse gases by human activity creates. Global Warming Potential is evaluated over different time horizons, being the most common 100 years (GWP100a).
[kg NMVOC eq]
Ozone, on the ground level, is toxic to humans in high concentrations. Photochemical ozone is formed by the reaction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the presence of heat and sunlight.
[kg Sb eq]
The depletion of abiotic resources is referred to the consumption of minerals, metals, water, and others and the value of the consumption of a substance is a measure of its scarcity, which depends on the amount of the material and the extraction rate.
[MJ]
The depletion of abiotic resources is referred to the consumption of fossil fuels and the value of the consumption of a substance is a measure of its scarcity, which depends on the amount of the material and the extraction rate.
[m3 world eq. deprived]
Indicator of the relative amount of water used, based on regionalized water scarcity factors.
[kg CFC-11 eq]
CFC and other halocarbon emissions have depleted the stratospheric ozone layer. This reduces its ability to prevent ultraviolet (UV) light from entering the earth’s atmosphere, leading to a rise in the amount of carcinogenic UVB light.


SDG 8
SDG 9

SDG 12

SDG 13


